Introduction
Sustainable agriculture is a holistic approach to farming that prioritizes environmental conservation, social responsibility, and economic viability. This article explores financial strategies that farmers can adopt to promote sustainability, ensuring the longevity of agricultural practices while minimizing their impact on the environment.
Investing in Soil Health
Importance of Healthy Soil for Sustainable Agriculture
Healthy soil is the foundation of sustainable agriculture. This section discusses the critical role soil health plays in promoting crop productivity, nutrient cycling, and overall ecosystem balance.
Strategies for Soil Improvement and Conservation
Investing in soil improvement and conservation practices is essential. We explore strategies such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and reduced tillage that contribute to maintaining and enhancing soil health.
Adopting Agroecological Practices
Overview of Agroecology and Its Benefits
Agroecology integrates ecological principles into agricultural systems. We delve into the principles of agroecology and how adopting such practices can enhance sustainability.
Implementing Agroecological Practices for Sustainable Farming
Practical implementation of agroecological practices involves diversifying crops, integrating livestock, and optimizing resource use. This part explores how farmers can apply agroecological principles for sustainable farming.
Precision Farming Technologies
Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
Technology plays a crucial role in advancing sustainable agriculture. We discuss the significance of precision farming technologies in optimizing resource use, reducing waste, and improving overall efficiency.
Precision Farming Tools and Their Impact on Resource Efficiency
Precision farming tools, including GPS-guided tractors and sensors, contribute to resource efficiency. This section explores the financial benefits of adopting precision farming technologies.
Diversification of Crops
Benefits of Crop Diversification
Crop diversification is a key strategy for sustainable agriculture. We discuss the benefits, including reduced pest pressure, improved soil health, and enhanced resilience to environmental changes.
Strategies for Implementing Diversified Cropping Systems
Implementing diversified cropping systems requires thoughtful planning. This part explores strategies for farmers to diversify their crops, balancing economic considerations with sustainability goals.
Water Conservation and Irrigation Efficiency
Significance of Water Conservation in Agriculture
Water scarcity is a growing concern in agriculture. We explore the importance of water conservation and the role it plays in ensuring sustainable farming practices.
Efficient Irrigation Methods for Sustainable Water Use
Efficient irrigation methods, such as drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting, contribute to sustainable water use. This section discusses how adopting these methods can result in long-term financial benefits.
Integration of Livestock in Farming Systems
Importance of Integrated Farming Systems
Integrating livestock into farming systems has multiple benefits, including nutrient cycling and diversified income streams. We explore the financial advantages of incorporating livestock sustainably.
Sustainable Practices in Livestock Management
Implementing sustainable practices in livestock management involves proper grazing, waste management, and animal welfare. This part discusses how farmers can integrate livestock sustainably.
Financial Support and Incentives for Sustainable Agriculture
Government Programs Supporting Sustainable Farming
Governments often provide financial support for sustainable farming. We explore existing programs that offer subsidies, grants, and incentives for adopting environmentally friendly practices.
Financial Incentives and Subsidies for Adopting Sustainable Practices
Farmers can benefit from financial incentives and subsidies for transitioning to sustainable agriculture. This section outlines available options and how to access them.
Organic Farming and Certification
Transitioning to Organic Farming
Organic farming aligns with sustainable principles. We discuss the process of transitioning to organic farming and the financial considerations involved.
The Importance of Organic Certification and Its Financial Implications
Organic certification adds value to farm products. We explore the importance of certification for market access and the potential financial implications for farmers.
Collaborative Farming and Farmer Cooperatives
Benefits of Collaborative Farming
Collaborative farming offers advantages such as shared resources and knowledge. This part explores the financial benefits of farmers coming together for collective efforts.
Formation of Farmer Cooperatives for Shared Resources and Support
Farmer cooperatives provide a platform for shared resources and support. We discuss how collaborative initiatives can enhance financial sustainability for individual farmers.
Education and Training Programs
Importance of Education for Sustainable Agriculture
Education is a crucial component of promoting sustainable farming practices. We explore the role of education in creating awareness and fostering a culture of sustainability.
Training Programs for Farmers on Sustainable Practices
Training programs equip farmers with the knowledge and skills needed for sustainable agriculture. This section discusses the availability of training programs and their impact on financial sustainability.
Building Resilience to Climate Change
Climate Change Challenges in Agriculture
Climate change poses challenges for agriculture, from unpredictable weather patterns to increased pest pressure. We discuss the financial implications and strategies for building resilience.
Financial Strategies for Building Resilience and Adaptation
Farmers can adopt financial strategies to build resilience to climate change. This part explores insurance options, diversification, and other measures to mitigate risks.
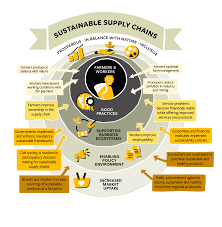
Market Access and Sustainable Supply Chains
Connecting Sustainable Farmers with Markets
Market access is vital for the economic sustainability of farmers. We explore strategies to connect sustainable farmers with markets that appreciate and support their practices.
Strategies for Establishing and Maintaining Sustainable Supply Chains
Establishing and maintaining sustainable supply chains require collaboration. This section discusses strategies for farmers to engage with stakeholders and ensure the sustainability of their products.
Monitoring and Evaluation of Sustainable Practices
Importance of Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Continuous monitoring and evaluation are essential for assessing the impact of sustainable practices. We explore the financial benefits of tracking progress and making informed decisions.
Tools for Assessing the Financial Impact of Sustainable Practices
Various tools and metrics help farmers assess the financial impact of sustainable practices. This part introduces farmers to tools that can aid in evaluating the economic benefits of sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, financial strategies play a pivotal role in promoting sustainable agriculture. From investing in soil health to adopting agroecological practices and accessing government incentives, these strategies contribute to the long-term viability of farming while safeguarding the environment.
FAQs
- How does crop diversification contribute to sustainable agriculture?
- Crop diversification reduces pest pressure, improves soil health, and enhances resilience to environmental changes, contributing to the overall sustainability of agriculture.
- What financial incentives are available for farmers transitioning to organic farming?
- Financial incentives for organic farming may include subsidies, certification support, and market access benefits, which vary by region and government programs.
- How can collaborative farming benefit individual farmers financially?
- Collaborative farming offers benefits such as shared resources, knowledge exchange, and collective marketing efforts, leading to improved financial sustainability for individual farmers.
- What role does education play in promoting sustainable farming practices?
- Education creates awareness and imparts knowledge about sustainable farming practices, enabling farmers to make informed decisions that contribute to their financial sustainability.
- How can farmers assess the financial impact of their sustainable practices?
- Farmers can use various tools and metrics to assess the financial impact of sustainable practices, including evaluating resource efficiency, market access, and long-term economic benefits.