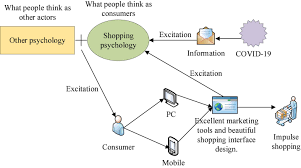
Introduction
The world of commerce is not only about fulfilling needs; it’s also about the art and science of persuasion. Consumer impulse buying, a phenomenon deeply ingrained in the psychology of shopping, plays a pivotal role in the success of businesses. This article delves into the psychology behind impulse buying, exploring the factors that influence consumers to make unplanned purchases and the strategies businesses employ to capitalize on this behavior.
Instant Gratification and Pleasure Seeking
At the heart of impulse buying is the human desire for instant gratification and pleasure. When consumers spot a product that promises immediate satisfaction or triggers positive emotions, the impulse to purchase becomes compelling. Businesses tap into this psychology by creating marketing messages and product displays that evoke joy, excitement, or a sense of indulgence.
FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
The fear of missing out is a powerful motivator for impulse buying. Consumers, driven by the desire to be part of trends or exclusive experiences, often make impulsive purchases to avoid the perceived loss of not owning a particular product. Limited-time offers, exclusive deals, and product scarcity are strategies businesses employ to amplify the FOMO effect and drive impulse purchases.
Emotional Triggers and Storytelling
Emotions play a significant role in consumer decision-making. Businesses leverage emotional triggers through storytelling, connecting their products to consumers’ aspirations, memories, or desires. When a product narrative resonates emotionally, it heightens the likelihood of impulse buying as consumers are driven by their emotional connection to the brand or the product’s story.
Convenience and Accessibility
The ease of making a purchase contributes to impulse buying behavior. The more convenient and accessible a product is, the more likely consumers are to make spontaneous decisions. Online shopping platforms, one-click purchases, and mobile payment options enhance the convenience factor, enabling consumers to act on their impulses swiftly.
Influence of Social Proof
Social proof, or the influence of others’ opinions and behaviors, can trigger impulse buying. When consumers see positive reviews, testimonials, or witness others making quick purchases, it creates a sense of validation and trust. Businesses strategically showcase social proof through user-generated content, influencer endorsements, and customer testimonials to reinforce the idea that the product is worth an impulsive buy.
Discounts, Promotions, and Limited-Time Offers
The psychology of scarcity and urgency plays a key role in impulse buying. Businesses frequently use discounts, promotions, and limited-time offers to create a sense of urgency and scarcity, compelling consumers to act swiftly to secure a perceived bargain. The fear of missing out on a great deal often leads to impulsive purchasing decisions.
Sensory Appeal and Product Presentation
The physical and visual appeal of a product can trigger impulse buying by engaging consumers’ senses. Vibrant packaging, enticing displays, and product samples in-store captivate the senses and create a desire to experience the product immediately. Online retailers leverage high-quality product images, videos, and interactive content to evoke a sensory response and drive impulsive clicks.
Cognitive Biases and Decision Heuristics
Cognitive biases and decision heuristics influence how consumers process information and make decisions. Anchoring, where consumers rely heavily on the first piece of information encountered, and the scarcity heuristic, which places higher value on scarce items, are examples. Businesses capitalize on these biases through strategic pricing, emphasizing discounts, and creating a perception of product exclusivity.
Loyalty Programs and Rewards
Loyalty programs and rewards contribute to impulse buying by offering immediate incentives. Consumers, enticed by the prospect of earning points, discounts, or freebies, are more likely to make unplanned purchases to capitalize on the immediate gratification provided by loyalty rewards. Businesses design loyalty programs strategically to encourage repeat impulsive buying behavior.
Personalization and Targeted Marketing
Personalized marketing appeals directly to individual preferences and needs, increasing the likelihood of impulse buying. Businesses leverage data analytics and customer insights to tailor marketing messages, recommendations, and promotions. When consumers feel that a product is personalized to meet their specific desires, they are more inclined to make impulsive decisions.
Cognitive Dissonance Reduction
Consumers often experience cognitive dissonance, a state of discomfort resulting from conflicting thoughts or beliefs. Impulse buying can serve as a means to alleviate this discomfort. After making an unplanned purchase, consumers may rationalize their decision to align with their self-image or values, reducing cognitive dissonance and reinforcing the idea that the impulse buy was justified.
Gamification and Interactive Experiences
Gamification elements and interactive experiences enhance the appeal of impulse buying. Businesses introduce elements of fun, challenges, or interactive features that engage consumers and make the purchasing process enjoyable. Gamified shopping apps, limited-time challenges, and interactive product demonstrations create an environment where impulse buying becomes an exciting and rewarding experience.
Conclusion
The way prices are presented can influence consumer perceptions and trigger impulse buying. Strategies like charm pricing (setting prices just below a round number), bundling, and tiered pricing appeal to consumers’ perception of value. Prices ending in “9” or “99,” for example, cr.