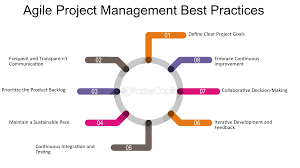
In the fast-paced realm of project management, where change is the only constant, the Agile methodology has emerged as a transformative approach that values flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Agile project management is not just a set of processes; it’s an art form that empowers teams to navigate uncertainties and deliver valuable outcomes in a dynamic environment. In this exploration, we delve into the principles, practices, and nuances that define the art of Agile project management.
Adaptability to Customer Needs
Agile emphasizes adaptability to customer needs. Unlike traditional contract-focused approaches, Agile promotes continuous collaboration with customers throughout the project. This ensures that the delivered product aligns closely with customer expectations, leading to higher satisfaction and success.
Flexible Contractual Agreements
Agile embraces flexible contractual agreements. Instead of rigid contracts, Agile methodologies encourage flexible arrangements that accommodate changes in project scope. This customer-centric approach fosters a partnership mindset, prioritizing collaboration over strict contractual negotiations.
Responding to Change over Following a Plan
Agile values responding to change. Rather than rigidly adhering to a predefined plan, Agile methodologies embrace the ability to respond to changing requirements. This flexibility allows teams to adjust their course based on evolving insights and project dynamics.
Iterative and Incremental Development
Agile projects follow iterative and incremental development. Breaking down projects into small, manageable iterations ensures continuous refinement and adaptation throughout the project lifecycle. This iterative approach allows for constant improvement.
Roles and Responsibilities
The Scrum framework defines clear roles and responsibilities. Roles such as Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team each have distinct responsibilities, fostering collaboration and accountability within the team.
Sprints and Daily Stand-ups
Scrum introduces the concept of sprints—time-boxed development cycles. Daily stand-up meetings keep the team synchronized, address challenges, and ensure everyone is aligned towards common goals.
Visualizing Workflow
Kanban emphasizes visualizing the workflow on a Kanban board. This visual representation helps teams identify bottlenecks, manage work in progress, and optimize the flow of tasks.
Continuous Delivery
Kanban promotes a continuous delivery model. Features or enhancements are released as soon as they are ready, allowing for quicker responses to customer needs and market changes.
Supporting the Team
Agile leaders adopt a servant leadership style, focusing on supporting the team. They remove obstacles and provide the necessary resources for the team to succeed, fostering a culture of collaboration and empowerment.
Facilitating Collaboration
Agile leaders facilitate collaboration among team members. They create an environment where ideas can flow freely, and individuals feel empowered to contribute their expertise.
Iterative Planning and Review
Agile embraces iterative planning and review. Regular reviews and retrospectives allow teams to continuously learn from their experiences and adapt their plans accordingly.
Continuous Improvement Mindset
Agile leaders instill a continuous improvement mindset. They encourage teams to reflect on their processes and seek ways to enhance efficiency, quality, and collaboration in each iteration.
Avoiding Overwhelm
Balancing flexibility and structure is crucial to avoid overwhelm. While Agile offers flexibility, teams must strike the right balance to prevent chaos and ensure effective project management.
Setting Clear Expectations
Clear communication and well-defined expectations are critical. Managing stakeholder expectations and ensuring alignment with Agile principles are necessary for successful project outcomes.
Efficient Delivery of Value
Agile’s focus on delivering incremental value ensures efficient project delivery. Releasing functioning parts of a project faster keeps stakeholders engaged and ensures alignment with evolving requirements.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Agile methodologies prioritize open communication and collaboration. This breaks down silos and fosters a shared responsibility among team members, leading to enhanced collaboration.
Swift Response to Changes
Agile equips teams with the ability to adapt quickly to changing requirements. This agility ensures that the project remains aligned with business goals even in dynamic environments.
Conclusion
The iterative nature of Agile allows for continuous testing and validation, reducing the risk of discovering significant issues late in the project. This enables early course correction.